
If you are a beginner in fabrics and you are starting to make your own clothes or you want to create your own brand, then you must read this complete blog. It will help you to understand the complete vocabulary of fabrics and easily speak with your suppliers.
Ten years back, the following vocabulary was also completely absent from our knowledge, but we are now constantly using them as a fabric supplier.
There are many different types of fibers. It is important to learn properties to choose the perfect fabric that suits your design and the touch you want to get.
Different Types of Fibers?
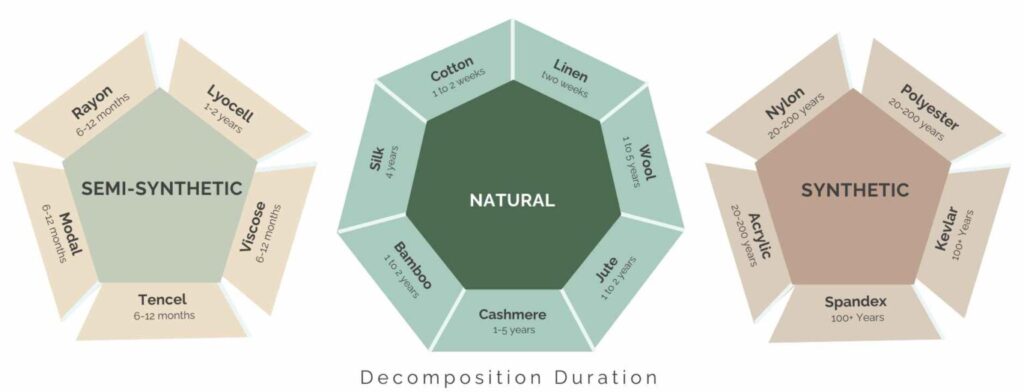
Fabrics are mainly divided into 3 different types of fibers that are natural, semi synthetic and synthetic. Let’s learn more about them one by one.
1. Natural Fabrics
Natural fabrics are extracted from plants and animals. These fabrics are more and more used due to the softness and feel of the fabric. Let’s explain with some examples.
Plant-based: Organic cotton, linen, wood, hemp, bamboo, jute, and many more grow easily in the soil. It is naturally grown and easily biodegradable.
Animal-based: It includes silk, wool, cashmere, alpaca, and more. These natural fabrics decompose easily, are very comfortable, eco-friendly, and breathable.
In 2024, global production of natural fibers reached around 33 million tonnes which is 1.3 million tonnes more than the year before
2. Semi Synthetic Fabrics
Semisynthetic fabrics are made from natural materials. But that has been altered chemically. To be clearer, the fabrics come from plants (bamboo, wood, hemp, jute, and more); then they are modified using modern technology. Some of the examples include rayon, viscose, modal, lyocell, and more. These types of materials are considered semi-eco-friendly because the source is natural, but to produce them, they will need strong chemicals.
3. Synthetic Fabrics
Synthetic fabrics are made from petroleum. They need a lot of harsh chemicals and energy to be produced at all stages of the production line. Some examples of famous types of synthetic fabrics include olefin fabric, microfiber, fleece, and more. These materials will not naturally decompose in the environment. These fabrics are now the most popular products in the textile industry because they are easy to use, cheap, and can get many types of finishing with the use of chemicals (wrinkle-resistant, waterproof ). Apart from this, it can absorb water easily and also dry quickly.
How is a fabric made?
Firstly, let’s understand how fabrics are made. A fabric is made with multiple yarns. In order to create the fabric, these yarns will be woven, knitted, or knotted together, then the structure will be formed. The end material has a variety of applications, such as garments, accessories, home furnishings, and many more.
The process of fabric manufacturing undergoes several steps, from harvesting to the final finish. It can be created in many different ways, depending on the different types of fabrics. Let’s go in-depth through each step one by one.
1. Fiber cultivation/extraction
This step is also referred to as fiber harvesting. Here, all the raw materials are obtained from natural sources. The natural fibers come from plants (like cotton, linen, hemp, bamboo, wood, and jute), animals (such as wool or silk), or petroleum.
2. Yarn production
Once the fiber is harvested, it needs to be spun into yarn before it can be woven or knitted into fabric. The raw fiber is cleaned and carded (combed to separate and align the fibers), then it is spun into yarn. In the traditional method, this process could be done by hand, and now it is mostly done through machines. Spinning twists the fibers together to create a long and continuous yarn.
3. Fabric Weaving or Knitting
After the yarn is produced, it needs to be turned into fabric. This process is done through weaving or knitting.
Weaving is the process of interlacing yarns vertically and horizontally. The vertical threads are known as the warp, and the horizontal threads are known as the weft. The weaving is done by using a machine called a loom. To give a tight structure, the warps are stretched out on a loom, and the weft is passed through them.
Knitting is the process of connecting loops or stitches of one continuous long thread using large needles. This can be done by hand or by machine.
4. Washing (RFD—Ready for Dyeing)
After weaving or knitting, it is important to wash the fabric. The washing process is called RFD (ready for dyeing). Almost all natural fibers contain impurities (like waxes, pectines, and natural oils) that need to be removed before the dyeing stage. After removing all these impurities, the fabric is ready for dyeing.
5. Dyeing/Printing
Once the fabric is clean, it is ready to be dyed. Dyeing gives the fabric its color, and it can be done using various methods, with natural or synthetic dyes/pigments.
Have a small sentence about different dyeing and printing (block print, screen print, digital print).
Natural dyeing means that it is dyed using natural ingredients derived from plants (Indigofera, indigo, turmeric, marigold petals, pomegranate, walnut hulls, cochineal, and more) or minerals (alum salt, earth iron).
The other origin of colors, which is the most common use, is derived from petroleum; it is called synthetic dyes.
6. Final finishing
Often, the fabric undergoes a finishing process after being done with its dyeing process. This process modifies the fabric texture and appearance. It makes the fabric feel smoother and softer. This process is made by the use of chemicals to get the following types of finishing, for example, flame retardant, UV protection, waterproof, wrinkle-free, and many more. At the end of the process, the fabric is ready for use in various products.
Difference between Woven and knit?
Woven
Woven is made by interlacing two sets of yarns. It is thick compared to knitting and wind-resistant. Due to its better elastic character, it can be used in the manufacturing of shirts, trousers, jeans, denim jackets, and many more.
Knit
Knitted fabrics are made by looping a single yarn. It is used in making t-shirts, sweaters, leggings, socks, hats, and more. As compared to woven, it can be more flexible and breathable.

Summary
People can easily make informed decisions whenever they are choosing fabrics and other projects. Overall, this blog article, PART 1, covers the essential vocabulary related to fabrics and fibers, and we hope it helped you gain knowledge in this field. It addresses all the key factors you need to know to discuss with any fabric supplier.
Are you searching for quality and sustainable fabrics?
We supply natural and ready-to-dye fabrics worldwide. Green Tailor offers a large range of biodegradable fabrics made from various natural fibers (organic cotton, recycled cotton, kala cotton, linen, silk, wild silk, and wool). You can discover here all the fabrics.
Contact us today by mailing us at [email protected]. Our expert team is always ready to assist you till the end. Make your natural and sustainable collection now!
